News 

How to realize the automated production of sheet metal manufacturing
Category:answer Publishing time:2025-12-19 12:25:56 Browse: Times
With the rapid development of Industry 4.0, the manufacturing industry is transforming and upgrading towards intelligence and automation. Sheet metal manufacturing, as an important link in mechanical manufacturing, is widely used in many fields such as automobiles, aerospace, electronic equipment, and home appliances. Traditional sheet metal processing depends heavily on manual operations and experience judgment, leading to problems such as low efficiency, unstable quality, and high costs. Therefore, achieving automated production in sheet metal manufacturing has become an inevitable trend in industrial development.
One, The Necessity of Sheet Metal Manufacturing Automation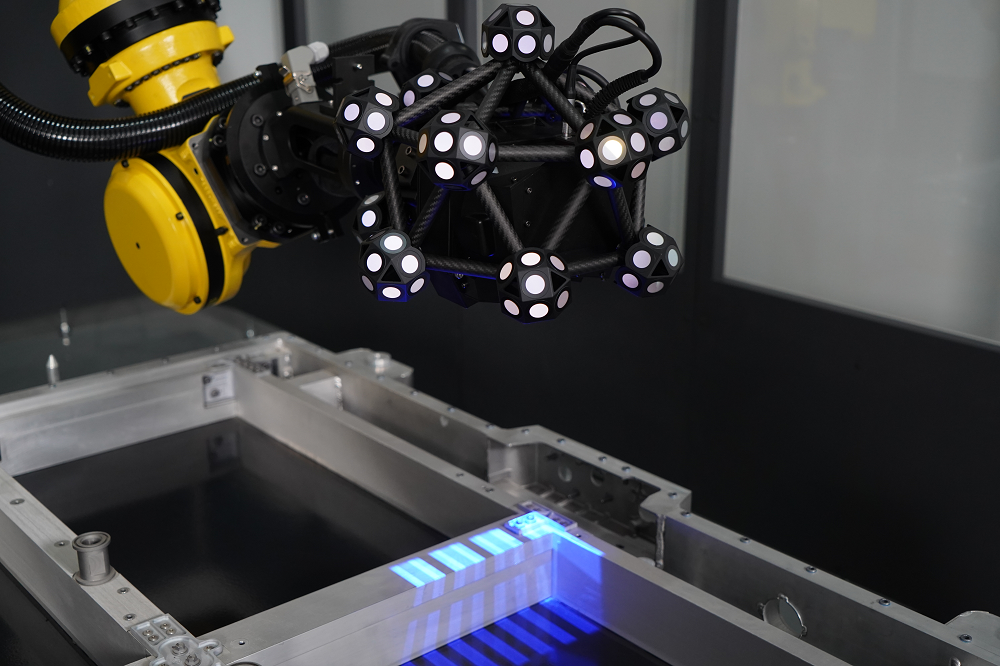
Firstly, automation can significantly improve production efficiency. In traditional sheet metal processing, operations such as stamping, shearing, bending, and welding often require manual loading and unloading, parameter adjustment, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. Automated equipment can operate continuously, reducing manual intervention, and shortening the production cycle.
Secondly, automation helps to improve the consistency of product quality. Manual operations are easily affected by fatigue and skill levels, while automated systems can ensure the stability of each process through precise parameter control, reducing waste rate and rework rate.
In addition, automation can reduce labor costs and safety risks. The introduction of robots and mechanical arms in high-intensity, high-risk working environments can effectively ensure worker safety and alleviate the problem of labor shortage.
Two, Key Technologies for Achieving Sheet Metal Manufacturing Automation
1. Application of numerical control (CNC) equipment
Advanced equipment such as CNC stamping machines, laser cutting machines, and CNC bending machines are the core tools for achieving automation. They can complete complex processing tasks according to preset programs, improving accuracy and efficiency.
2. Robot integration
Industrial robots are widely used in processes such as loading and unloading, handling, welding, and stacking. For example, during the bending process, robots can automatically grab sheets according to instructions and complete multi-angle bending, significantly improving production flexibility.
3. Integration of MES and ERP systems
The application of Manufacturing Execution System (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems enables digital management of production planning, material scheduling, and process monitoring, promoting the transition of sheet metal manufacturing to intelligent manufacturing.
4. Visual recognition and artificial intelligence
Through machine vision systems, the positioning, identification, and detection of workpieces can be realized, assisting robots in completing precise operations. The introduction of AI algorithms can also optimize processing paths and improve resource utilization.
Three, Implementation Path of Sheet Metal Manufacturing Automation
1. Gradually promote automation transformation
Enterprises can start with key processes, such as introducing automatic stamping machines or laser cutting machines, and then gradually expand to the integration of the entire production line.
2. Focus on talent cultivation and technical support
Automation requires higher technical requirements for operators, so enterprises need to strengthen employee training and establish good cooperative relationships with equipment suppliers and software service providers.
3. Construction of a digital management platform
By building a unified data platform, integrating information such as equipment, processes, and quality, full-process visualization and intelligent control can be realized.
Four, Conclusion
The automation of sheet metal manufacturing is not only an important means to enhance corporate competitiveness, but also an inevitable choice to adapt to the development of intelligent manufacturing in the future. Although challenges such as high investment costs and high technical thresholds may be faced in the implementation process, through scientific planning and continuous innovation, enterprises can fully occupy the initiative in the fierce market competition and achieve high-quality and efficient development.
With the rapid development of Industry 4.0, the manufacturing industry is transforming and upgrading towards intelligence and automation. Sheet metal manufacturing, as an important link in mechanical manufacturing, is widely used in many fields such as automobiles, aerospace, electronic equipment, and home appliances. Traditional sheet metal processing depends heavily on manual operations and experience judgment, leading to problems such as low efficiency, unstable quality, and high costs. Therefore, achieving automated production in sheet metal manufacturing has become an inevitable trend in industrial development.
One, The Necessity of Sheet Metal Manufacturing Automation

Firstly, automation can significantly improve production efficiency. In traditional sheet metal processing, operations such as stamping, shearing, bending, and welding often require manual loading and unloading, parameter adjustment, which is time-consuming and prone to errors. Automated equipment can operate continuously, reducing manual intervention, and shortening the production cycle.
Secondly, automation helps to improve the consistency of product quality. Manual operations are easily affected by fatigue and skill levels, while automated systems can ensure the stability of each process through precise parameter control, reducing waste rate and rework rate.
In addition, automation can reduce labor costs and safety risks. The introduction of robots and mechanical arms in high-intensity, high-risk working environments can effectively ensure worker safety and alleviate the problem of labor shortage.

Two, Key Technologies for Achieving Sheet Metal Manufacturing Automation
1. Application of numerical control (CNC) equipment
Advanced equipment such as CNC stamping machines, laser cutting machines, and CNC bending machines are the core tools for achieving automation. They can complete complex processing tasks according to preset programs, improving accuracy and efficiency.
2. Robot integration
Industrial robots are widely used in processes such as loading and unloading, handling, welding, and stacking. For example, during the bending process, robots can automatically grab sheets according to instructions and complete multi-angle bending, significantly improving production flexibility.
3. Integration of MES and ERP systems
The application of Manufacturing Execution System (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems enables digital management of production planning, material scheduling, and process monitoring, promoting the transition of sheet metal manufacturing to intelligent manufacturing.
4. Visual recognition and artificial intelligence

Through machine vision systems, the positioning, identification, and detection of workpieces can be realized, assisting robots in completing precise operations. The introduction of AI algorithms can also optimize processing paths and improve resource utilization.

Three, Implementation Path of Sheet Metal Manufacturing Automation
1. Gradually promote automation transformation
Enterprises can start with key processes, such as introducing automatic stamping machines or laser cutting machines, and then gradually expand to the integration of the entire production line.
2. Focus on talent cultivation and technical support
Automation requires higher technical requirements for operators, so enterprises need to strengthen employee training and establish good cooperative relationships with equipment suppliers and software service providers.
3. Construction of a digital management platform
By building a unified data platform, integrating information such as equipment, processes, and quality, full-process visualization and intelligent control can be realized.
Four, Conclusion
The automation of sheet metal manufacturing is not only an important means to enhance corporate competitiveness, but also an inevitable choice to adapt to the development of intelligent manufacturing in the future. Although challenges such as high investment costs and high technical thresholds may be faced in the implementation process, through scientific planning and continuous innovation, enterprises can fully occupy the initiative in the fierce market competition and achieve high-quality and efficient development.




























