News 

How to formulate inspection standards for quality control
Category:answer Publishing time:2025-09-26 08:55:03 Browse: Times
In modern industrial production, quality control is an important link to ensure that products meet design requirements and customer expectations. As the core basis for quality control, inspection standards directly affect whether products are qualified. Therefore, formulating scientific and reasonable inspection standards is a key factor for enterprises to improve product quality and enhance market competitiveness.
I. Clarify Product Requirements and Standard Bases
The first step in formulating inspection standards is to clarify the technical requirements that the product should meet. This includes national or industry standards, customer contract requirements, product design drawings, and relevant laws and regulations. Enterprises need to sort out the quality standards required to be achieved based on the product's purpose, performance indicators, safety specifications, etc. On this basis, combined with their own production technology and equipment capabilities, they can determine executable inspection items and indicators.
II. Identification of Critical Quality Characteristics
When formulating inspection standards, it is necessary to identify the critical quality characteristics (Critical to Quality, CTQ) of the product. These characteristics usually include dimensional accuracy, material composition, appearance defects, functional performance, etc. For each critical characteristic, clear inspection methods, detection frequency, and tolerance range should be set to ensure effective monitoring during the production process.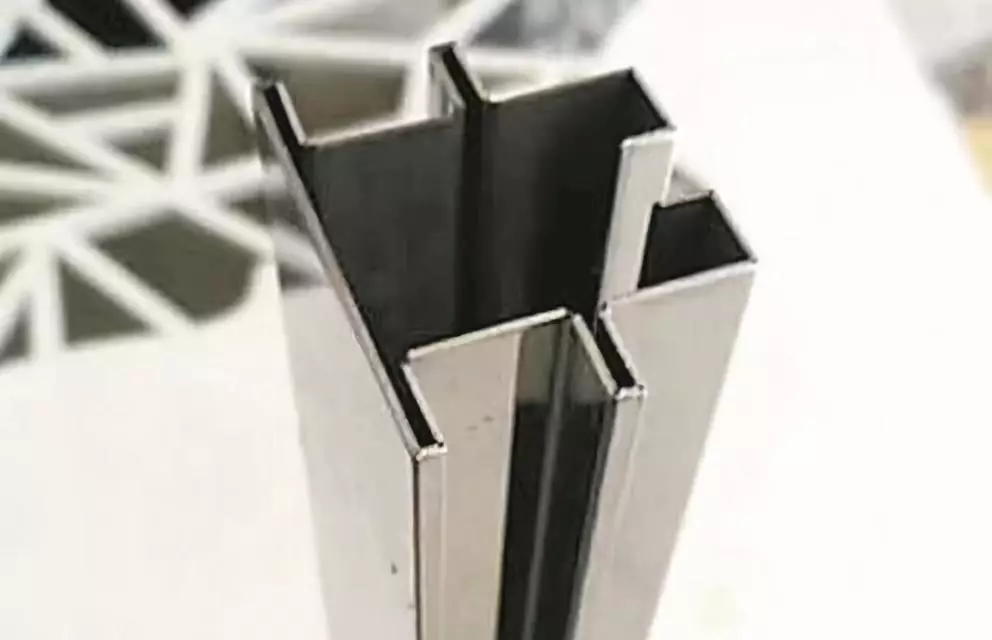
III. Establishment of a Graded Inspection System
To improve inspection efficiency and accuracy, enterprises should establish a multi-level inspection system. Generally, it includes: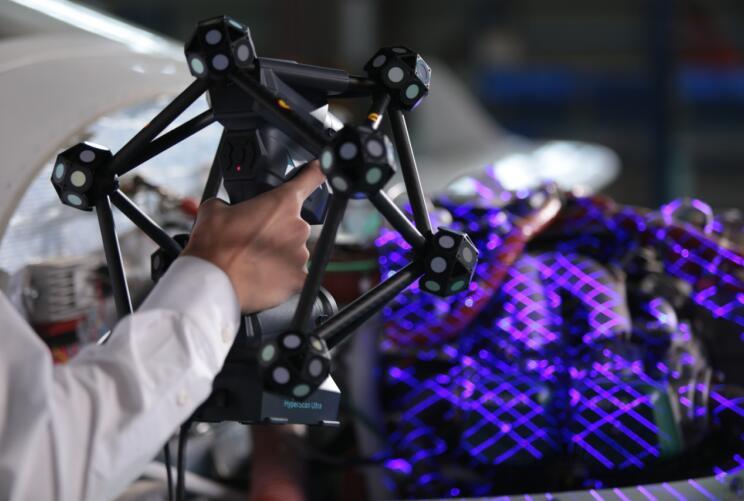
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspect raw materials and components upon entering the factory to prevent poor materials from entering the production process;
2. Process Inspection (IPQC): Set key control points in the production process to monitor product quality in real-time;
3. Final Inspection (OQC): Carry out comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure that the products meet the standards upon leaving the factory;
4. Shipment Inspection: Conduct sampling inspection before product delivery to prevent quality loss during transportation.
IV. Selection of Appropriate Inspection Methods and Tools
The formulation of inspection standards also needs to consider the feasibility and accuracy of inspection methods. Common inspection methods include visual inspection, measurement tool detection, chemical analysis, non-destructive testing, etc. Enterprises should choose appropriate methods and equipment according to product quality characteristics and detection purposes, and train inspectors to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of data.
V. Continuous Improvement and Standard Update
Quality control is not immutable. With the changes in market demand, production technology, and technological progress, inspection standards should also be adjusted accordingly. Enterprises should establish a sound feedback mechanism, continuously optimize inspection standards through customer feedback, internal quality data analysis, and quality audits, and achieve continuous improvement.
Conclusion
In summary, establishing scientific and reasonable inspection standards is the foundation of the quality control system. It not only helps to ensure product quality but also improves production efficiency and reduces quality risks. When enterprises formulate inspection standards, they should combine actual conditions, pay attention to systematicity and operability, and continuously optimize and improve them in practice to adapt to the constantly changing market environment and technical requirements.
In modern industrial production, quality control is an important link to ensure that products meet design requirements and customer expectations. As the core basis for quality control, inspection standards directly affect whether products are qualified. Therefore, formulating scientific and reasonable inspection standards is a key factor for enterprises to improve product quality and enhance market competitiveness.
I. Clarify Product Requirements and Standard Bases
The first step in formulating inspection standards is to clarify the technical requirements that the product should meet. This includes national or industry standards, customer contract requirements, product design drawings, and relevant laws and regulations. Enterprises need to sort out the quality standards required to be achieved based on the product's purpose, performance indicators, safety specifications, etc. On this basis, combined with their own production technology and equipment capabilities, they can determine executable inspection items and indicators.
II. Identification of Critical Quality Characteristics
When formulating inspection standards, it is necessary to identify the critical quality characteristics (Critical to Quality, CTQ) of the product. These characteristics usually include dimensional accuracy, material composition, appearance defects, functional performance, etc. For each critical characteristic, clear inspection methods, detection frequency, and tolerance range should be set to ensure effective monitoring during the production process.

III. Establishment of a Graded Inspection System
To improve inspection efficiency and accuracy, enterprises should establish a multi-level inspection system. Generally, it includes:

1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspect raw materials and components upon entering the factory to prevent poor materials from entering the production process;
2. Process Inspection (IPQC): Set key control points in the production process to monitor product quality in real-time;
3. Final Inspection (OQC): Carry out comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure that the products meet the standards upon leaving the factory;
4. Shipment Inspection: Conduct sampling inspection before product delivery to prevent quality loss during transportation.
IV. Selection of Appropriate Inspection Methods and Tools
The formulation of inspection standards also needs to consider the feasibility and accuracy of inspection methods. Common inspection methods include visual inspection, measurement tool detection, chemical analysis, non-destructive testing, etc. Enterprises should choose appropriate methods and equipment according to product quality characteristics and detection purposes, and train inspectors to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of data.

V. Continuous Improvement and Standard Update
Quality control is not immutable. With the changes in market demand, production technology, and technological progress, inspection standards should also be adjusted accordingly. Enterprises should establish a sound feedback mechanism, continuously optimize inspection standards through customer feedback, internal quality data analysis, and quality audits, and achieve continuous improvement.
Conclusion
In summary, establishing scientific and reasonable inspection standards is the foundation of the quality control system. It not only helps to ensure product quality but also improves production efficiency and reduces quality risks. When enterprises formulate inspection standards, they should combine actual conditions, pay attention to systematicity and operability, and continuously optimize and improve them in practice to adapt to the constantly changing market environment and technical requirements.




























